Ang Kompleksidad at Dinamika ng Supply Chain ng Industriya ng Kimika
Ang industriya ng paggawa ng kimika ay isang maraming layer na sistema na kumakatawan sa buong proseso ng produksyon, mula sa ekstraksiyon ng mga row material hanggang sa produksyon at distribusyon ng huling produkto. Ang artikulong ito ay umaasongs sa estraktura ng supply chain ng industriya ng kimika, pagsusuri sa kanyang pangunahing segment at mga characteristics na nagdidisenyo sa kanyang kumplikadong anyo.
Panimula sa Supply Chain ng Industriya ng Kimika
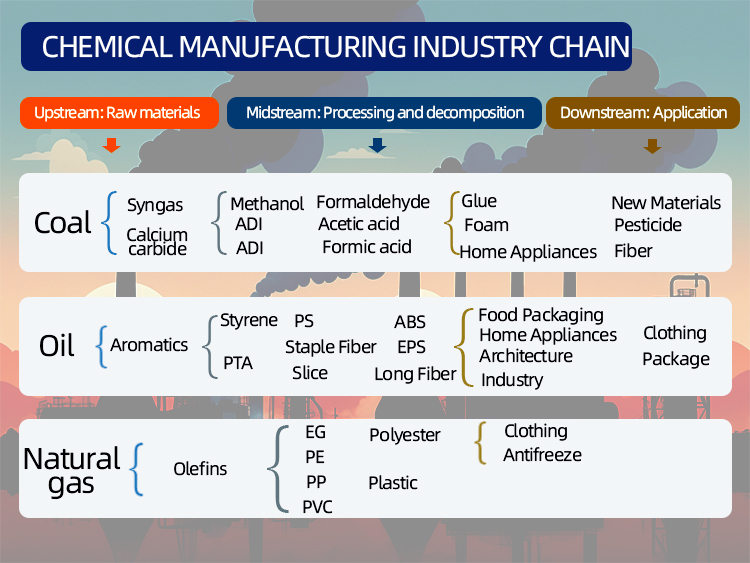
Ang supply chain ng industriya ng kimika ay tipikal na nahahati sa tatlong pangunahing bahagi: upstream raw material supply, midstream production and processing, at downstream product applications.
1. Upstream Raw Material Supply
Ang unang bahagi sa supply chain ng industriya ng kimika ay naglalagay sa pagkakamit at pagproseso ng pangunahing materyales na row. Kasama sa mga ito ang mga natural resources tulad ng crude oil, natural gas, at coal, na mahalaga para sa paggawa ng malawak na uri ng mga produkto ng kimika. Gayunpaman, ang mga pangunahing inorganikong kimika tulad ng hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, at ammonia, pati na rin ang mga organikong kimika tulad ng polymers, plastics, at rubber, ay kinukuha mula sa fase na ito.
Kasama rin sa upstream operations ang ekstraksiyon ng mineral resources at ang pag-refine ng mga row materials, na kritikal para sa pagsasangguni ng mga specialty chemicals na ginagamit sa iba't ibang industriya.
2. Midstream Production and Processing
Ang katapusan ng gitna ay doon nangyayari ang pagbabago ng mga row na materyales sa mga panggitnang produkto o derivatives. Ito ang yugto sa industriya ng kimika, kung saan ang mga pangunahing materyales ay dumadaan sa iba't ibang kimikal na proseso upang lumikha ng mga kimikal, plastik, ubo, sintetikong serbes, at marami pa. Ang mga produkto tulad ng kimikal na serbes, pesticides, at ubo ay sinusintesis noong panahong ito, na naglilingkod bilang isang tulay sa pagitan ng ekstraksyon ng row na materyales at ang market ng final product.
Halimbawa, ang petrochemical plants sa pagbago ng crude oil sa mahalagang mga produkto tulad ng ethylene, propylene, at benzene. Ang mga ito intermediates ay dinadala pa para lumikha ng mga materyales tulad ng Polimero , na ginagamit sa maramihong industriyal at consumer applications.
3. Downstream Produkto Applications
Ang sektor ng downstream ay nakatuon sa huling gamit ng mga produkto ng kimika, at ang mga aplikasyon nito ay umiabot sa isang malawak na aray ng industriya. Suporta ng industriya ng kimika ang maraming sektor ng end-user tulad ng automotive, healthcare, agriculture, electronics, at construction.
Halimbawa, sa industriya ng automotive, mahalaga ang mga kimika sa paggawa ng paint, plastics, at rubber components. Sa agriculture, tulad ng fertilizers at pesticides, nagtutulak ang mga kimika sa pagtaas ng ani. Pati na rin, ang high-tech electronics ay dependent sa mga kimika para sa paggawa ng semiconductors at batteries.
Ang pagka-uugat ng mga produkto ng kimika sa mga industriya na ito ay nagpapakita ng malaking impluwensya ng industriya ng kimika sa pang-araw-araw na buhay at sa mga industriyal na sektor.

Mga Punong Sub-Sektor sa Industriya ng Kimika
Bukod sa mga pangunahing segment, maaaring hatiin pa ang industriya ng kimika sa mga espesyal na sub-sektor, bawat isa ay mayroong mga produkto o industriya.
-
Mga petro-kimikal
Ang mga produkto ng petrokemika ay bumubuo sa likod ng industriya ng kemikal sa buong mundo. Ito ay nanggagaling mula sa petroleum at natural gas at ginagamit sa paggawa ng plastik, sintetikong serbes, rubbers, at iba pang mahalagang kemikal para sa iba't ibang sektor. Ang proseso ng pag-refine ay nagbibigay ng mga produkto tulad ng ethylene, propylene, at benzene, na napakalaki sa maraming aplikasyon. -
Mga Kamanghang Kimikal
Ang mga kemikal na maikli ay kilala dahil sa kanilang mataas na halaga at itinuturo sa maliit na dami. Kasama sa mga kemikal na ito ang mga tagapagligtas ng farmaseytikal, agro-kemikal tulad ng pesticides, at iba pang espesyal na kemikal. Dahil sa kanilang kumplikado at presisyon sa sintesis, madalas na may mataas na marahal ang mga kemikal na maikli at sumusukat sa mga industriyang kailangan ng advanced na pormulasyon. -
Mga abono
Hindi maaalis ang mga pagkakain sa agrikultura, kasama ang mga produkto tulad ng nitrogen fertilizers, phosphate fertilizers, at potassium fertilizers na sumusupporta sa pagsasagawa ng pagkain sa buong mundo. Mga kemikal na ito ay mahalaga sa pagsulong ng paglago ng prutas at integram sa pagtugon sa pangangailangan ng pagkain ng dumadaghang populasyon. -
Plastik at Rubber
Ginagamit ang mga produkto ng plastik at rubber nang malawak sa parehong consumer goods at industriyal na aplikasyon. Ang paggawa ng polyethylene, polypropylene, at polystyrene ay sumusuporta sa iba't ibang industriya tulad ng packaging, automotive, at elektronika. Ang mga polymers na ito ay mantikang materyales na tumutugon sa pang-araw-araw na produkto at mataas na katayuan na industriyal na komponente.
Mga Katangian ng Supply Chain ng Industriya ng Kimika
Nakikilala ang supply chain ng industriya ng kimika para sa kanyang kumplikadong anyo, cross-linkages, at rehiyonal na distribusyon.
-
Kumplikado
Ang industriya ng kimika ay naglalaman ng isang malawak na hanay ng mga row materials, intermediate products, at end-use applications. Ang mga interaksyon sa pagitan ng iba't ibang segmento ay masyadong interdependent, lumilikha ng isang kumplikadong sistema kung saan ang mga disruptiya sa isang antas ay maaaring mag-apekto sa buong chain. Ang pangangailangan ng precision at kontrol sa bawat yugto ng produksyon ay gumagawa ng chemical supply chain. -
Mga Cross-Linkages
Ilan sa mga produkto sa industriya ng kimika ay maaaring gawaing mula sa maramihang row materials, humahantong sa mga interconnections sa pamamagitan ng iba't ibang segmento. Halimbawa, ang polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ay maaaring gawin sa pamamagitan ng dalawang iba't ibang proseso: isa ay batay sa petroleum at ang iba ay batay sa coal. Ang mga cross-linkages ay nagbibigay-daan sa industriya ng kimika upang umadaptive sa mga pagbabago sa availability at demand ng row materials. -
Regional Distribution
Heograpikamente, ang paggawa ng kimika ay nakakonsentra sa mga rehiyon na mayaman sa mga yugto ng anyo o kung saan may malaking demand. Sa Tsina, halimbawa, ang mga probinsya tulad ng Shandong at Jiangsu ay kilala dahil sa kanilang malawak na industriya ng petrokimika dahil sa kanilang malapit sa mga pangunahing pabrika at may access sa mahalagang yugto. Ang lokasyon ng produksyon ng kimika ay malakas na naiimpluwensya ng pagkakaroon ng yugto, imprastraktura, at demand ng merkado.
Kokwento
Ang supply chain ng industriya ng kimika ay isang dinamiko at network ng mga proseso, mula sa ekstraksiyon ng anyo hanggang sa produksyon ng mga advanced na produkto ng kimika. Sa pamamagitan ng pag-unawa sa estraktura at operasyon ng industriyang ito, maaaring mas ma-navigate ng mga negosyo at politikong tagapagtataguyod ang kanilang mga hamon at oportunidad. Sa pamamagitan ng kanyang malawak na aplikasyon sa mga industriya mula sa agrikultura hanggang sa elektronika, patuloy na maging pinakamaliwanag ng modernong paggawa at teknolohikal na progreso ang industriya ng kimika.
Mga produktong may kalakasan mula sa aming kompanya:

Fluorescent Brightener 378 CAS 40470-68-6
Ethylmagnesium Bromide CAS 925-90-6
Sodium ethoxide CAS 141-52-6
2,5-DIMETHOXY-BETA-NITROSTYRENE CAS 40276-11-7
CHROMIUM(III) PHOSPHATE CAS 7789-04-0
PETMP CAS 7575-23-7
4-tert-Butylbenzoic acid CAS 98-73-7
Irgacure 819 Photoinitiator 819 CAS 162881-26-7
Hydrotalcite CAS 11097-59-9
POLY(HEXAMETHYLENE DIISOCYANATE) CAS 28182-81-2
BISPHENOL A DIGLYCIDYL ETHER RESIN CAS 1675-54-3
glycolic acid cas 79-14-1 (99% pulbos o 70% solusyon)
Azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) CAS 78-67-1
glyoxal cas 107-22-2
PINDUTIN UPANG PUMUNTA SA PAGBABIHIS NG PRODUKTO 


 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 KA
KA
 LA
LA
 MN
MN
 KK
KK
 LB
LB