1,2-Dichloroethane (CAS 107-06-2): Essential industrial solvent
|
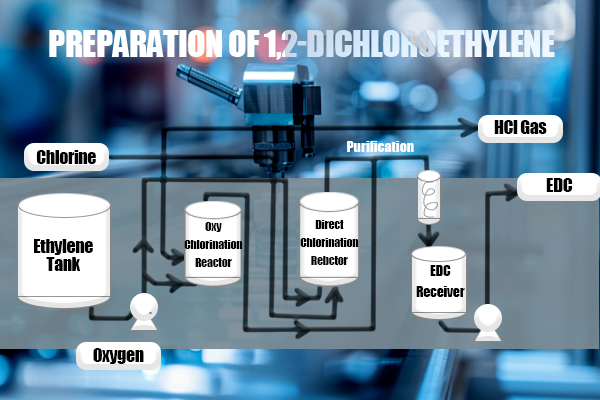
1,2-Dichloroethane (CAS 107-06-2) also known as ethylene dichloride (EDC), is a significant chemical compound widely used across various industries. As a versatile organic compound, it plays a crucial role in producing polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and serves as a solvent in multiple chemical processes. This article provides a comprehensive overview of 1,2-dichloroethane, delving into its production processes, key applications, and necessary safety considerations. Production of 1,2-Dichloroethane The production of 1,2-dichloroethane is dominated by two main industrial processes: direct chlorination and oxychlorination of ethylene. These methods are essential for meeting global demand, particularly in manufacturing vinyl chloride monomer (VCM).
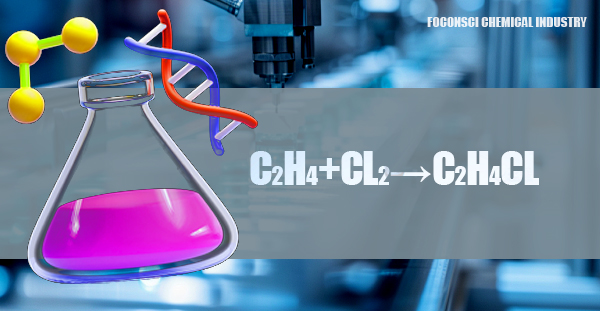
In the direct chlorination process, ethylene (C₂H₄) reacts with chlorine gas (Cl₂) to form 1,2-dichloroethane (C₂H₄Cl₂). This reaction typically occurs in the presence of a ferric chloride (FeCl₃) catalyst at temperatures between 50-70°C. The process is highly efficient, producing 1,2-dichloroethane with minimal by-products and high purity. The chemical equation for the reaction is:
This method is favored for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it the predominant process in industrial settings.
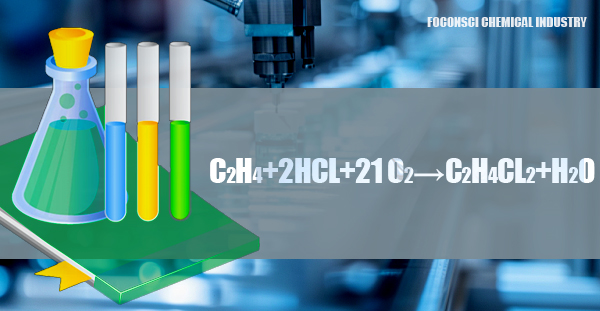
The oxychlorination process is an alternative method that uses ethylene, hydrogen chloride (HCl), and oxygen (O₂) to produce 1,2-dichloroethane. This reaction, catalyzed by a copper-based catalyst at temperatures of 200-300°C, also generates water as a by-product. The reaction can be summarized as:
The oxychlorination process is particularly advantageous for its ability to utilize hydrogen chloride, a by-product of other chemical processes, thus enhancing overall efficiency. Applications of 1,2-Dichloroethane 1,2-Dichloroethane's diverse applications make it a cornerstone in the chemical industry, particularly in the production of PVC and as a solvent in various processes.
The primary use of 1,2-dichloroethane is as a precursor to vinyl chloride monomer (VCM), which is subsequently polymerized to form polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The thermal cracking of 1,2-dichloroethane at around 500°C produces VCM and hydrogen chloride. Given the widespread use of PVC in products ranging from pipes to medical devices, the demand for 1,2-dichloroethane remains high.
1,2-Dichloroethane is a highly effective solvent, used in the extraction and purification of organic compounds. It is also employed in the production of adhesives, paints, and coatings, where its solvent properties enhance the performance and application of these products.
Beyond its role in VCM production, 1,2-dichloroethane serves as a crucial intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals, including ethyleneamines and various solvents. Its reactivity with nucleophiles allows it to participate in the production of a wide range of organic compounds, contributing to its versatility.
The solvent properties of 1,2-dichloroethane also make it useful as a degreasing agent for metals and a cleaning solvent in the textile and automotive industries. However, due to its toxicity and environmental impact, the use of 1,2-dichloroethane in these applications has decreased over time. Safety Considerations Given its widespread use, understanding the safety considerations associated with 1,2-dichloroethane is essential. This compound is highly toxic and poses significant health risks if not handled properly.
1,2-Dichloroethane is classified as a hazardous substance. Exposure can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact, leading to acute symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, and respiratory distress. Prolonged exposure can cause more severe health issues, including liver and kidney damage. Therefore, stringent safety protocols are necessary when handling this chemical.
1,2-Dichloroethane is also a concern from an environmental perspective. It is highly volatile and can contribute to air and water pollution if not managed correctly. Industries that use 1,2-dichloroethane are required to implement robust waste management practices to minimize environmental contamination. Contact us
|
 |


 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 KA
KA
 LA
LA
 MN
MN
 KK
KK
 LB
LB